
Another definition of management accounting can be derived from the process of identifying, measuring, analyzing, interpreting, and communicating information to help pursue an organization’s goals. Without GAAP, investors might be more reluctant to trust the information presented to them by public companies. Without that trust, fewer transactions and higher transaction costs could result, ultimately weakening the economy. GAAP also helps investors analyze companies by making it easier to perform “apples-to-apples” comparisons between one company and another, allowing for more accurate and consistent analysis. The international financial reporting standards (IFRS), set by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB), is an alternative to GAAP that is widely used worldwide.
Difference between financial and managerial accounting
- Budget is the decisive factor that sets the tone for organizing the smooth operations of a company.
- This system follows the double entry system, which ensures that for every financial transaction, equal and opposite changes are recorded in 2 or more accounts, maintaining balance within the company’s financial records.
- This improves the quality of financial reporting and helps the management make better strategic decisions as they have a clear picture of the company’s financial health.
- Her copy and content writing experience prior to this role includes education, non-profit, technology, building products, and other industries.
- Financial accounting reports on a business’s profitability (and, therefore, efficiency), whereas managerial accounting reports specifically on what is causing problems and how to fix them.
- Managerial accounting doesn’t focus on precise valuations but on how assets and liabilities add to the company’s overall productivity and profitability.
- They reduce orders for low-margin items and negotiate new terms with suppliers, boosting margins across 40% of SKUs.
It gets easier for a business to run its financial operations when they have the necessary data to manage day-to-day operations. Managerial accounting provides these tools and insights to help a business continuously monitor and analyze its financial performance. In this way, managerial accounting forms the foundation for sound financial management so businesses can operate efficiently and stay competitive – all while achieving sustainable growth. Financial accounting is designed for external users such as investors, creditors, and regulatory bodies. Financial statements help these outside parties make informed decisions about investments, lending money, or evaluating the company’s compliance with regulations.
e. Risk Management
It involves accurately valuing assets and liabilities through the balance sheet to reflect true financial position. The reason is that it can affect everything from the company’s share price in the stock market to its ability to secure loans from external institutions. Reports generated through managerial accounting are highly detailed and focus on a particular department or operational activity to provide data that can help managers improve overall internal performance.
How Managerial and Financial Accounting Are Similar
An accounting manager vs. controller focuses on providing detailed reports and data analysis that are customized to meet the specific needs of managers. Unlike financial accounting, which follows generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) and international accounting standards, managerial accounting lacks a standardized framework. This can lead to variations in accounting methods, reporting formats, and performance metrics across different organizations and industries. An organisation needs accountants in both these specialties for the best results. Certified Public Accountants are trained in financial accounting, while Certified Outsource Invoicing Management Accountants are trained in managerial accounting. It records the daily transactions within the organization as well as between the organization and other external parties.
Flexible Budgeting
Most importantly, it ensures that businesses and their financial reports meet regulatory requirements to maintain transparency. Managerial accounting (also known as cost accounting or management accounting) is a branch of accounting concerned with the identification, measurement, analysis, and interpretation of accounting information. Managerial accounting helps company management make informed operational and business decisions.

HighRadius Record-to-Report Solution helps businesses achieve and maintain GAAP compliance by automating key financial processes such as journal entries, account reconciliations, and financial reporting. By ensuring accuracy, consistency, and timely completion of tasks, the SOX Compliance Software supports GAAP’s requirements for standardization and transparency. Whether it is financial accounting or managerial accounting – a business needs both to survive and grow. Financial accounting caters to measuring the overall performance, while managerial accounting gives you insights into making organizational decisions. Many modern enterprises still view managerial and financial accounting as different functions, which limits their ability to fully leverage the benefits their integration can bring.

Integration and Importance in Business: Combining Managerial and Financial Accounting

The key differences between managerial accounting and financial accounting relate to the intended users of the information. Whether they are managerial accountants or financial accountants, they spend much of their time keeping the books. They are responsible for accurately recording every transaction that a company makes, whether it’s paying a contractor or buying a new machine. Beyond internal management, financial accounting plays a crucial role in regulatory compliance and transparency.
Efficiency
Financial accounting reports a company’s performance for a specific period of time and does it in the most straightforward way does managerial accounting follow gaap possible. For this task, managerial accountants having excellent command over cost accounting provide tremendous services, as they calculate overhead charges and figure out the expenses along with the production cost. No doubt, the success of a business depends on smart decisions, whereas management accounting can make a big difference. Managerial accountants are not required to adhere to Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) since their reports will be used within the company, not with external parties. Managerial accounting is different from financial accounting; it prioritizes flexibility and relevance rather than compliance.
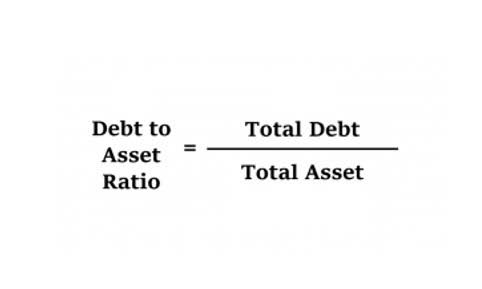
As such, it’s meant to transform financial data into decision-making intelligence for company leaders. Managerial accounting is the branch of accounting focused ledger account on providing internal management with relevant financial and non-financial information to assist in planning and decision-making. Unlike financial accounting which is aimed at external stakeholders, managerial accounting delivers detailed reports tailored to the specific needs of managers within an organization. These reports can include budgets, forecasts, cost analyses, and performance evaluations. Financial accounting is the branch of accounting focused on recording, summarizing, and reporting a company’s financial transactions.
- The payback period can be calculated by dividing the expected cash flow per year by the initial investment.
- These reports study the impact of estimates on the company’s operational productivity and profitability.
- Your reporting will play a major role in the financial decisions they take, and you will get to be involved in exciting company improvements.
- Managerial accounting incorporates non-financial performance metrics to provide a holistic view of organizational performance.
- In this particular type, accountants make the subcategories of cost that cover direct, indirect, variable, and fixed costs.
- If a corporation’s stock is publicly traded, its financial statements must follow rules set by the U.S.
- Managerial accounting provides relevant financial and non-financial information to managers and decision-makers within an organization, enabling them to make informed choices and effectively manage the business.
Measures how much money is left from each sale after variable costs to cover fixed costs and profit. The path to becoming a managerial accountant isn’t easy, but it’s well worth the effort. GAAP — or Generally Accepted Accounting Principals — are a set of standards that govern corporate accounting. Using this information, accounting professionals create budgets, policies, strategies, plans, and recommendations that they then present to the executive leadership teams at their organizations. Managerial accountants are the closest a company can get to hiring a fortune teller.